
Use the General tab to name and describe the data source.
#ODBC MANAGER WINDOWS DRIVER#
The Microsoft ODBC Driver for DB2 Configuration dialog contains five tabs. In the Create New Data Source dialog, click Microsoft ODBC Driver for DB2, and then click Finish. In the ODBC Data Source Administrator dialog, click Add. To add a data source for the ODBC Driver for DB2 using the ODBC Data Source Administrator. You can reset options by clicking Configure in any driver setup dialog box.Ĭlick Remove after selecting a data source. Adding a file data source is slightly different from adding user or system data sources.ĭepending on your requirements, you might find it necessary to reconfigure data sources. For example, if you create a data source for a set of DB2 tables that contain customer information, you might name the data source "Customers." Applications typically display data source names for users to choose from. Give each data source a name that uniquely identifies that data source. It is possible to add multiple data sources, each one associating a driver with some data you want to access by using that driver. Using the ODBC Data Source Administrator, you can add, modify, and delete data sources, as described in the following table. In Administrative Tools, click ODBC Data Sources.
#ODBC MANAGER WINDOWS WINDOWS 8#
To open the ODBC Data Source Administrator in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012. In Administrative Tools, click Data Sources (ODBC). In Control Panel, click Administrative Tools. To open the ODBC Data Source Administrator in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2. Each of these data sources has a tab in the ODBC Data Source Administrator dialog box. User and system data sources are collectively known as machine data sources because they are local to a computer. File data sources are stored in C:\Program Files\Common Files\ODBC\Data Sources. File data source names are not identified by dedicated registry entries instead, they are identified by a file name with a. These data sources need not be dedicated to a user nor be local to a computer.
#ODBC MANAGER WINDOWS DRIVERS#
System DSNs are registered in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE registry.įile DSNs are file-based sources that can be shared among all users who have the same drivers installed and therefore have access to the database. The system or any user with privileges can use a data source set up with a system DSN. System DSNs are local to a computer rather than dedicated to a user. They are registered in the HKEY_CURRENT_USER registry. User DSNs are local to a computer and can be used only by the current user. The types of data sources that can be used are described in the following table. Use the ODBC Data Source Administrator to add, configure, and delete data sources from your system. Using the ODBC Data Source Administrator, you can add/modify/remove connections for use with the Microsoft ODBC Driver for DB2.ĭata sources are the databases or files accessed by a driver and are identified by a data source name (DSN).
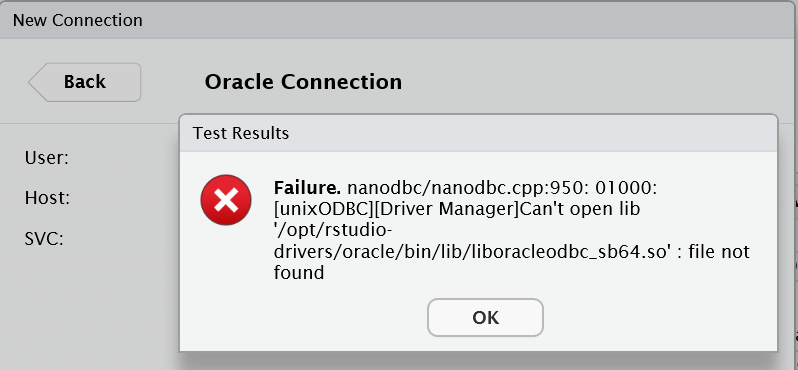
Beginning in Windows 8, the icon is named ODBC Data Sources, and on 64-bit operating systems there is a 32-bit and 64-bit version. This application is located in the Windows Control Panel under Administrative Tools. The Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator manages database drivers and data sources.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
